서론
연구의 필요성
신생아사망률의 가장 큰 원인은 조산으로 인한 미숙(prematurity)이지만(Anderson & Warren, 2011), 신생아 집중치료기술의 발달로 과거 생존이 어렵다고 생각했던 출생 시 체중 1,500 g 미만의 저출생체중아의 생존율이 76.6% 이상으로 향상되고 24주 미만의 극소미숙아들이 소생함으로써 미숙아의 생존한계를 극복하고 있다(Lee, Kim, et al., 2010). 그리하여 1993년에는 6.6%이었던 신생아사망률이 2009년에는 1.7%로 눈에 띄게 감소하였다(Chung, Choi, & Bae, 2011).
미숙아 생존을 위한 치료와 간호는 주로 복잡하고 역동적인 병원 환경에서 이루어지지만(Anderson & Warren, 2011), 최근에는 가정에서도 산소치료와 심전도 모니터링 등이 가능해지고 있으며, 병원 운영의 효율성 증대를 위한 재원일수 단축으로 미숙아의 조기퇴원이 활성화되고 있다(Lee, Lee, & Shin, 2009). 이러한 미숙아의 생존률 증가와 조기퇴원의 양상은 가정에서 영아를 돌보는 상황이 증가됨을 의미한다. 그러나 미숙아는 생명유지와 관련된 문제와 더불어 뇌성마비, 발달지연, 감각인지장애, 그리고 행동장애 등과 같은 신경학적인 문제에 직면하기 때문에(Fanaroff & Martin, 2002; Yoon, 2007), 신생아집중치료실에서 퇴원하여 가정에서 영아를 돌보아야 하는 부모는 어려움에 직면하게 된다. 뿐만 아니라 여러 가지 건강문제로 미숙아는 퇴원 후에도 응급실을 이용하거나 재입원하게 되는 경우도 많아 미숙아 부모는 미숙아 양육에 대해 체계적이고 지속적인 정보를 제공받기 원한다(Kim & Shin, 2010).
국내에서는 미숙아의 신생아집중치료실 입원 시부터 퇴원 후까지 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 다양한 교육을 제공하고 부모의 만족도나 미숙아의 건강회복 등을 보고한 많은 간호연구가 있다(Han, 2001; Jang, 2005; Jung, 1999; Kim & Shin, 2010; Kwon & Kwon, 2007). 그러나 미숙아의 치료와 양육 방법이 변화 발전하고 있으며, 정보통신기술의 발달로 교육매체 역시 다양화되는 시점에서(De Gagne & Oh, 2012) 지금까지 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 하여 어떤 내용과 방법으로 미숙아 돌봄 교육이 이루어져왔는지의 전반적인 정리와 고찰이 필요하다고 생각한다. 이러한 고찰 결과 밝혀진 내용들은 앞으로 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 하는 교육 프로그램 개발에 기초 자료가 될 것이다. 그리하여 본 연구자들은 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 미숙아 돌봄 교육을 시행하고 그 결과를 보고한 모든 국내 연구문헌을 찾아서 통합적 고찰(integrative review) 방법으로 체계적인 분석을 하고자 하였다.
통합적 고찰은 기존의 체계적 문헌고찰에서 보다 확대된 개념으로 Whittemore와 Knafl (2005)이 제시한 문헌고찰방법이다. 통합적 고찰은 양적연구와 질적연구를 포함한 다양한 방법론적인 연구들을 아우르는 방법이다. 또한 통합적 고찰은 관심 현상들에 대한 다양한 시각들을 나타내는데 기여하고, 간호연구와 간호교육, 그리고 간호실무에 중요한 역할을 하고 있다(Oh, Kang, & De Gagne, 2012). 통합적 고찰에서 자료분석에 사용되는 분명하고 체계적인 연구방법은 연구의 편향성으로부터 보호하고, 특정 현상에 대한 개요와 정확한 결론을 도출하여 좀 더 깊은 이해를 제공한다(Whittmore & Knafl, 2005).
연구 방법
연구 절차
통합적 고찰의 절차는 Whittmore와 Knafl (2005)의 지침에 따라 4가지 단계로 이루어졌다. 첫 번째 단계는 문제인식을 통하여 연구의 목적이 분명하게 드러나도록 하는 것이다. 연구자들은 연구의 구체적인 목적을 결정함과 동시에 분석할 논문의 선정 기준과 제외 기준을 엄격하게 규정하였다. 두 번째 단계는 연구 주제에 맞는 의미 있고 적절한 모든 자료를 단계적으로 찾아내는 문헌검색과정이다. 이 단계에서는 검색된 논문의 정당성과 명확함이 드러날 수 있도록 문헌검색과정에서 쓰인 주요용어, 사용된 데이터베이스, 추가적인 검색 과정 등을 상세하게 기록하였다. 세 번째 단계는 데이터 평가과정으로 문헌검색과정에서 찾아낸 초기의 자료를 평가하는 것이다. 본 연구에서는 연구의 질 평가도구를 사용하여 1차 선정한 논문에 대한 질 평가를 실시하였으며, 각 논문의 연구주제의 부합성, 방법론적인 질적 수준, 정보로서 연구결과의 가치 등을 함께 평가하였다. 네 번째 단계는 기존의 원 자료를 편견 없이 해석하여 의미를 종합하는 데이터 분석과정이다. 이 과정에서 연구자들은 각자 논문을 읽고 분석하면서 각 자료마다 분야별로 분석한 내용을 기록하고 메모하였으며 매주 정기적인 회의시간을 거쳐 의견을 조율하였다. 그리고 연구의 결론을 테이블 또는 그림의 형태로 나타내고자 심혈을 기울였다.
자료 수집 과정
자료수집 및 분석기간은 2012년 8월 1일부터 10월 30일까지였으며 검색 데이터베이스는 한국교육학술정보원(www.riss4u.co.kr), 한국학술정보(kiss.kstudy.com), 한국의학논문데이터베이스(kmbase.medric. or.kr), 디비피아(www.dbpia.co.kr)였다. 논문 검색에 사용된 주요 핵심 단어는 ‘미숙아’, ‘미숙아 부모’, ‘미숙아 어머니’, ‘교육’, ‘간호’로 조합하였고, 찾아진 모든 연구논문은 원문을 확보하였다. 논문검색 데이터베이스에서 검색된 논문은 총 40편이었으며 중복으로 확인된 논문 14편을 제외하고 검색조건을 충족시킨 논문은 모두 26편이었다. 그 이후 원본을 확보하여 모두 꼼꼼히 읽으며 선정 기준 부합 여부를 확인하는 과정을 거쳤으며, 그 결과 14편이 제외되었다. 제외된 논문을 살펴보면 미숙아 부모의 교육 요구도 논문 1편, 미숙아를 대상으로 한 중재 연구 3편, 모유수유 실태와 같은 미숙아 관련 서술적 연구 9편, 학술 대회 발표 논문 1편이 있었다. 그리하여 초기 12편의 연구가 선정되었으며, 12편 연구의 참고문헌 목록을 검토하는 과정에서 직접 손으로 찾은 논문 4편이 추가로 포함되었다. 연구의 질 평가를 거쳐 최종적으로 본 연구에 사용된 연구는 16편으로 확정되었다(Figure 1).
연구의 질 평가
Whittemore와 Knafl (2005)에 의하면 통합적 고찰에서 논문의 질 평가는 매우 복잡하기 때문에 연구의 선정과 제외 기준을 엄격하게 적용하는 것이 가장 중요하다고 하였다. 본 연구에서는 우선적으로 심사위원의 심사를 거쳐 학술지에 게재되었거나 학위논문으로 발표된 논문만을 대상으로 하였으며, 통합적 고찰 연구를 게재한 경험(Oh et al., 2012)이 있는 연구자의 통찰력과 심도 있는 논의를 통해 선정과 제외 기준을 적용하였다. 뿐만 아니라 Bowling (2002)이 개발한 연구의 질 평가 도구를 사용하여 연구목적의 명료성, 연구설계, 각종 변수, 자료수집과 분석방법, 그리고 주요 결과 등으로 구분하여 평가하였다(Table 1). 그리하여 분석대상이 된 논문들은 연구주제가 명료하고, 연구방법과 절차가 연구목적에 부합하여 통계에 오류가 없으며, 의미 있는 연구결과가 도출되어 연구의 질 평가 결과 16편 모두 분석대상 논문으로 적절하다고 판단하였다.
연구 결과
본 연구에서 선정한 미숙아 부모를 위한 미숙아 돌봄 교육 연구 16편을 발표 연도별로 분류했을 때 1990년부터 2000년까지 1편(6.3%), 2001년부터 2004년까지 1편(6.3%), 2005년부터 2009년까지 9편(56.2%), 2010년 이후로는 5편이었다(31.2%). 논문의 출처는 박사논문 1편(6.3%), 석사논문 4편(25%), 간호학술지 게재 논문은 9편(56.2%)이었으며, 의학학술지 게재 논문이 2편이었다(12.5%). 연구설계는 유사실험 연구가 11편(68.8%)이며, 방법론적 연구로 교육 프로그램 개발연구가 5편(31.2%)이었다(Table 2).
Table 2.
Analysis of Research Papers Used in Studies (N=16)
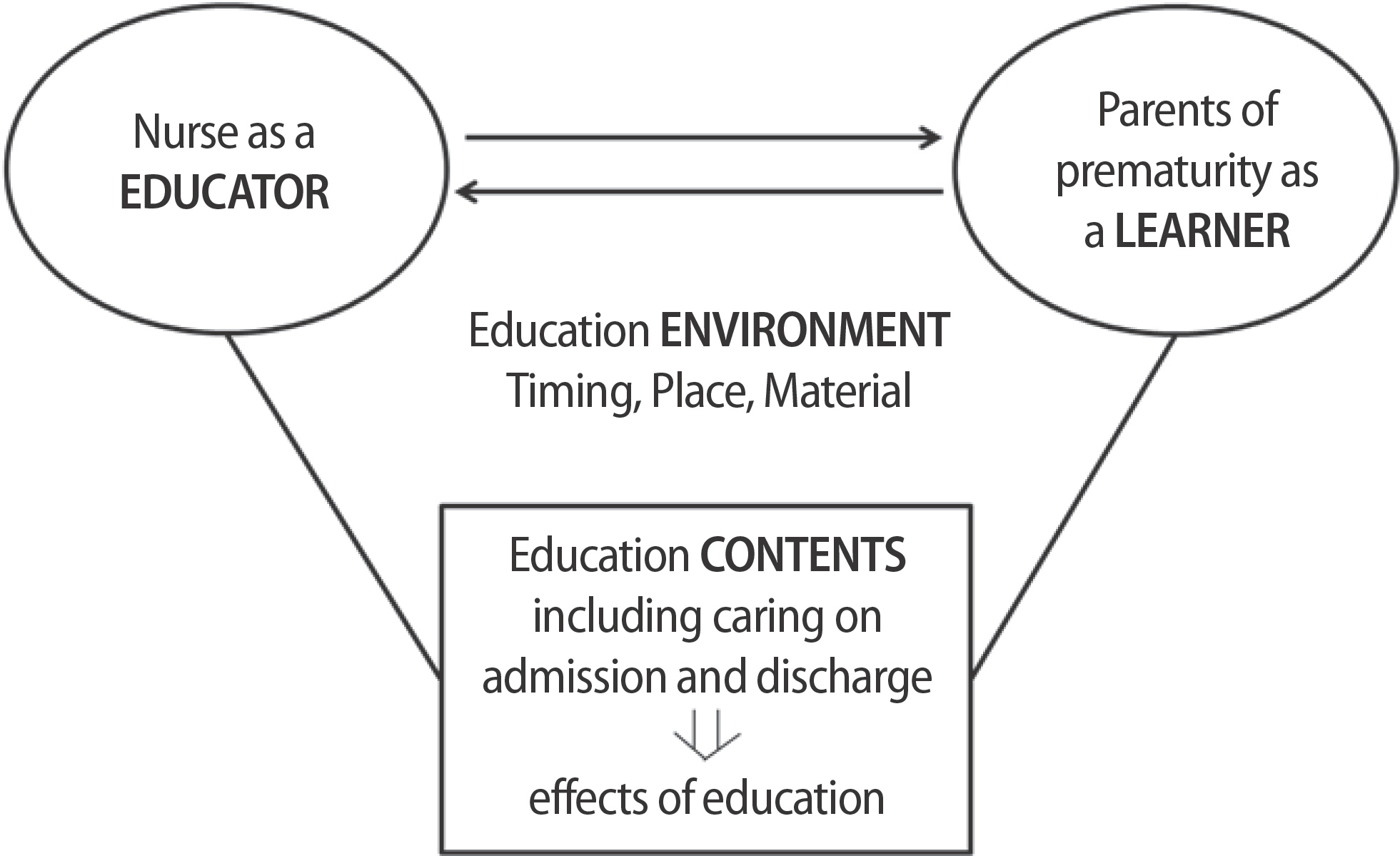
본 연구에서 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 한 미숙아 돌봄 교육 연구를 통합적으로 고찰한 결과 그 구성요소는 세 가지로 분석되었는데, 교육자로서의 간호사와 학습자로서의 미숙아 부모, 교육내용과 교육효과, 그리고 교육환경이었다. 이를 도식화하면 Figure 2와 같다.
교육자로서의 간호사와 학습자로서의 미숙아 부모
미숙아 돌봄 교육프로그램 개발연구 5편을 제외하고 나머지 모든 연구에서 미숙아 부모에게 교육과 정보를 제공하는 교육자의 역할을 하는 것은 간호사였다. 교육프로그램에서 미숙아 돌봄 교육 콘텐츠를 개발하는 것도 간호사였다. 그리고 본 연구에서 교육의 대상자를 미숙아 부모로 제한하였으나, 미숙아 부모 모두를 대상으로 하는 연구는 두 편이었으며 나머지 모든 연구는 그 학습자가 미숙아의 어머니였다.
미숙아 돌봄 교육내용과 교육효과
미숙아 돌봄 교육내용은 입원교육과 퇴원교육 두 가지로 분류되었다(Table 3). 입원교육에서는 신생아집중치료실의 환경을 소개하는 내용과 미숙아의 개념과 특성을 알려주는 내용이 포함되었다. 퇴원교육은 크게 네 가지로 분류되었는데, 첫 번째는 미숙아의 영양과 수유와 같은 가정에서의 기본적인 돌봄, 두 번째는 질병관리 측면으로 일반적인 질병, 응급상황, 그리고 기관지폐이형성증과 같이 특수질병 관리에 대한 교육이었다. 세 번째는 미숙아의 발달증진을 위한 자극과 발달교육, 마지막으로 미숙아 부모를 위한 정서적 지지였다.
Table 3.
Contents and Effects of Education for Parent with Premature Infants
미숙아 돌봄 교육 후 기대하는 효과는 미숙아의 건강증진과 미숙아 부모의 긍정적인 변화로 분류되었다. 미숙아의 건강증진 지표로는 건강상태, 성장측정이 있었고, 입원기간, 재입원율, 응급실 방문율이 포함되었다. 미숙아 부모에게 기대하는 효과는 부모로서의 역할 자신감 증진이 가장 많았고, 미숙아 어머니의 스트레스와 불안 감소, 모아상호작용 증진, 부모 역할 만족도, 그리고 모유수유 수행 향상 등이었다.
미숙아 돌봄 부모 교육환경
미숙아 부모를 대상으로 한 교육환경은 교육의 시기와 장소, 교육매체로 구분되었다. 교육의 시기는 입원 시부터 퇴원 후 한 달까지로 다양하였으며, 교육이 가장 많이 이루어지는 시기는 퇴원일로부터 1주일이었다. 교육장소는 주로 신생아집중치료실 내의 모유수유실이나 면담실이었으나 교육매체에 따라 가정에서 미숙아 부모가 스스로 콘텐츠를 보고 익히는 경우도 3편이 있었다. 교육매체는 소책자가 대부분을 차지하고 있으며 동영상과 파워포인트 자료를 활용하였다. 그 외 인터넷 웹사이트를 활용한 교육 3편, 스마트폰 어플리케이션을 개발하여 활용한 교육 1편이 있었고, 5편의 연구에서 전화를 이용한 교육이 이루어졌다(Table 1).
Table 1.
Chronological Summary of the Reviewed Research Papers (N=16)
| Authors (year) | Source | Research design | Partici-pants | Contents | Teaching tool | Education timing | Variables | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra (2012)* | Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Yeonsei University | Methodological study | 12 |
· Mother-Infant interaction · Symptom control (fever, hiccup, reflux, vomiting, diarrhea, seizure) |
Video | A week before discharge (3 times) |
· Mother-infant interaction · Maternal sensitivity · Maternal role confidence |
· Program using video was appropriate as a teaching method and education contents, especially mother-infant interaction, maternal sensitivity, maternal role confidence |
| Kang (2012)* | Unpublished master' thesis, Ewha Womans Univesity | Methodological study | 3 | · Nutrition of premature infants (breast feeding, gavage feeding) | Smart phone application | Unknown | No | · Nutritional program using smart phone application was easy to access, study without limitation of time, arouse interests |
| Choi (2011)* | Unpublished master' thesis, Keimyung University | Quasi experimental design | 42 |
· Understanding of premature infants · Basic infant care · Discharge education · Stimulation for growth and development · Symptom control · Supportive care for mothers |
Video, Powerpoint Phone call | 7-10days before discharge (3 times), 1 week later after discharge. |
· Maternal attachment · Rearing confidence · Rearing stress |
· Systematic information was an effective intervention to enhance maternal attachment, rearing confidence and decrease rearing stress. |
| Lee et al. (2010) | J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs, 16(2) | Quasi experimental design | 49 |
· Understanding of premature infants · Basic infant care · Symptom control · Special care (ostomy care, using SP02 monitor) · Follow up care |
Video, booklet | 5 days before discharge |
· Maternal confidence · Maternal anxiety |
· Program was efficient intervention method to boost maternal confidence, decrease anxiety. |
| Kim & Shin (2010) | J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs, 16(4) | Quasi experimental design | 32 |
· Understanding of premature infants · Basic infant care · Discharge education · Growth and development of infants · Symptom control · Precautions of premature infants |
Online community | 2 weeks before discharge, 4 weeks later after discharge |
· Parenting stress · Rearing confidence · Health problem for infants |
· Online community discharge program had the positive effect on decreasing parenting stress, increasing rearing confidence, decreasing health problem for premature infants. |
| Lee (2009) | J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs, 15(2) | Methodological study | NO |
· Understanding of premature infants · Symptom control · Basic infant care · Photos of infant and sharing information |
Website | Admission to 6 months later after discharge | No | · Website provided detailed, accurate and professional information on issues most parents of premature infants concern. |
| Lee & Kim (2008) | J Korean Acad Nurs, 38(1) | Methodological study | 15 |
· Understanding of premature infants · Symptom control · Basic infant care · Stress management for rearing · Community health resource · Growth and development of premature infants |
Website | 4 weeks |
· Teaching materials characteristics for program · Teaching system characterist for program · Satisfaction of learner |
· Program was a useful means to provide premature-care information to mothers.· Information was readily accessible and can varied and complex enough to help mothers of premature infants. |
| Cho et al. (2008) | J Kor Soc Qual Assur Health Care, 14(2) | Quasi experimental design | 85 |
· Symptom control · Basic infant care · Discharge education |
Panel, Booklet | Until baby's weight up to 2 kg (3 times) |
· Duration of hospitalization · Rearing confidence |
· Program was effect on decreasing duration of hospitalization increasing rearing confidence. |
| Lee (2007)* | Unpublished master'thesis, Sungkyunkwan University | Quasi experimental design | 191 |
· NICU admission education · Understanding of premature infants · Discharge education · Basic infant care · Symptom control · Follow up care · Supportive care for mothers |
Booklet, Phone call | 2-7 days later after a birth, 2-3 days later after discharge |
· Duration of hospitalization · Gestational age and weight at discharge · Breast feeding rate · Readmission rate · Rate of visiting to ER |
· Program was effect on decreasing duration of hospitalization, gestational age and weight at discharge · Program was help to increase breast feeding rate and decreased visiting emergency room rate |
| Kwon & Kwon (2007) | J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs, 13(1) | Quasi experimental design | 30 |
· Understanding of premature infants · Symptom control · Basic infant care · Discharge education · Supportive care for mothers |
Booklet, Model of newborn | 7-10 days before discharge to 4 weeks later after discharge (4 times) |
· Maternal role confidence · Parenting stress |
· Program was a efficient intervention method to boost the material confidence of mothers with premature infants and decrease their parenting stress. |
| Song et a (2007) | al. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health, 11(1) | Quasi experimental design | 32 |
· Basic infant care · Symptom control · Supportive care for mothers |
Phone call, Booklet | Discharged day to 2 weeks after discharge (4 times) |
· Maternal anxiety · Rearing confidence |
· Supportive care using telephone was effective method to decrease anxiety level and increase the rearing confidence in mothering role of premature infants. |
| Ma (2005)* | Unpublished master'thesis, Yonsei University | Methodological study | No |
· Information of BPD · Emergency situation with BPD (apnea, bradycardia, asphyxia)· Use of special equipment for BPD · General care |
Booklet | No | No | · Education was useful not only for the nurses working with parents of babies with BPD, but beneficial to new nurses and student nurses. |
| Kim (2005) | J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs, 11(4) | Quasi experimental design | 40 | · Massage for premature infants (importance, advantages, precautions, training of basic activities, babies’ signal) | Booklet, Video, Phone call | Before discharge to 4 weeks later after discharge |
· Growth of infants · Confidence, satisfaction in mothering role |
· Massage program enhanced growth of premature infants as well as enhancing the mother's confidence in her role as mothers. |
| Jang (2005) | J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs, 11(4) | Quasi experimental design | 32 |
· NICU admission education · Understanding of premature infants · Basic infant care · Symptom control |
Booklet | Within 1 week after admission to 1 week after discharge |
· Perceived stress · Maternal role confidence · Breast feeding practice |
· Program was the positive effect on decreasing the perceived stress level and increasing the breast feeding practice. |
| Han (2001) | J Korea Acd Soc of Home Care Nursing, 8(1) | Quasi experimental design | 21 |
· Basic infant care · Symptom control · Growth and development of infants · Supportive care for mothers · Mother-Infant interaction · Social resources |
Booklet, Video | A day before or discharge day, a week after discharge, 1 month corrected age, 3 months corrected age |
· Postpartum depression · Maternal self esteem · Infant care burden · HOME · Mother-infant interaction · Infant development |
· Intervention program of this study was very effective in enhancing the parenting for the mothers of low-birth weight infants, resulting in health promotion of low-birth weight infants. |
| Jung (1999) | J Korea Acad Child Health Nurs, 5(1) | Quasi experimental design | 19 |
· NICU admission education · Understanding of premature infants · Basic infant care · Symptom control · Growth and development of infants |
Booklet, Phone call | Admission to 2 weeks after discharge |
· Maternal stress · Maternal role strain · Maternal role performance |
· Program was the effective to decrease stress, maternal role strain and increase maternal role performance |
논의
최근 의학기술의 발달로 인한 신생아사망률의 감소는 미숙아의 생존과 가정으로의 복귀에 따른 가정에서의 미숙아 돌봄의 중요성으로 이어진다. 뿐만 아니라 저비용 고효율정책을 기조로 하는 보건의료정책과 의료수익증대의 차원에서 짧아진 재원기간으로 인해 미숙아 돌봄에 대한 부모 교육은 그 비중이 더욱 높아가고 있다(Lee et al., 2009). 본 연구는 미숙아의 신생아집중치료실 입원부터 퇴원 후에 이르기까지 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 하는 미숙아 돌봄 교육과 관련된 연구를 선정하여 통합적 고찰을 실시한 것이다. 본 연구결과 미숙아 부모 대상 미숙아 돌봄 교육의 구성요소는 교육자로서의 간호사와 학습자로서의 미숙아 부모, 미숙아 돌봄 교육내용과 교육효과, 미숙아 돌봄 부모 교육환경 등으로 분석되었다. 일반적으로 교육의 구성요소로는 인적요소, 학습요소, 환경요소로 구분할 수 있는데(De Gagne & Oh, 2012), 본 연구에서도 교육자와 학습자의 인적요소, 교육내용과 교육효과를 포함하는 학습요소, 그리고 교육 환경요소 등으로 분석되어 유사한 결과임이 확인되었다. 이에 연구결과 밝혀진 각각의 구성요소를 중심으로 논의하면서 추후 교육 프로그램 개발 방향을 모색하고자 한다.
본 연구에서 살펴본 모든 논문에서 미숙아 돌봄에 대하여 직접 교육을 담당하는 것은 간호사였다. 신생아집중치료실은 생명을 위협하는 건강문제를 경험하는 신생아에게 집중치료가 이루어지는 곳으로(Willis, 2008), 중환자를 다루는 집중치료실에서는 생존 위기에 처해 있는 환자를 대상으로 기본적인 위생 간호에서부터 높은 수준의 지적 판단이 필요한 특수 간호에 이르기까지 포괄적이고 숙련된 간호가 요구된다(Lee, Sung, Yi, Cho, & Kwon, 2007). Lee 등은 중환자실 간호사들은 교육자, 환자의 옹호자, 간호의 질 관리자, 직접 간호제공자 등의 순으로 간호업무를 수행한다고 보고하여 환자와 가족교육의 역할이 매우 중요함을 시사하였다. 전통적으로 환자와 가족을 대상으로 하는 교육은 경험이 많은 간호사가 수행하고 있으며(Kwon, Sung, Kwon, & Hwang, 2008), 본 연구에서도 역량이 있고 경험이 많은 일반간호사, 혹은 신생아 전문간호사가 미숙아 돌봄 부모교육을 담당하고 있었다(Lee, Oh et al., 2010). 그러나 집중치료실의 일반간호사가 교육을 담당하는 경우는 역할의 혼란과 중복을 초래하며, 이로 인해 간호사들은 잠재적인 역할갈등의 요소를 안고 있다(Wall, 2006). 간호의 전문화를 위한 노력으로 새로운 분야에서 많은 간호사의 역할이 개발되고 있고 간호에도 새로운 업무가 출현되고 있어 서로 다른 직종의 업무와 혼합되기도 하지만, 중증환자 간호의 효율성을 위해 교육과 상담을 전담으로 하는 교육간호사의 필요성은 더욱 높아지고 있다. 더욱이 간호사의 교육과 상담역할이 건강보험 급여항목으로 인정됨에 따라 그 역할은 한층 더 확대되고 있기 때문에(Sung et al., 2009), 신생아 전문간호사 중에서도 부모와 가족교육을 전담하는 교육 역할의 인정이나 교육간호사의 확보가 이루어져야할 것이다.
한편 본 연구에서 미숙아 돌봄 교육에서 대부분의 학습자는 미숙아의 어머니였다. 이는 많은 가정에서 영아를 돌보는 주양육자가 어머니이기 때문에 당연한 결과라고 생각되나 영아 돌보기에 대한 아버지 역할의 중요성이 강조되고 있고(Oh, Oh, & Nam, 2005), 많은 취업 여성이 경제적인 부담감이나 양육자에 대한 신뢰 등의 문제로 친조모나 외조모가 주양육자 혹은 보조양육자로서 양육을 담당하는 사례도 늘고 있기 때문에(Oh, 2007), 아버지나 조모들을 위한 미숙아 돌봄 교육도 이루어져야 할 것이다. 이는 미숙아 돌봄 교육의 학습자로서 직접 미숙아를 돌봄에 참여하는 각 구성원을 위한 맞춤형 교육프로그램이 필요함을 시사하는 것이다.
미숙아 돌봄 교육의 내용으로는 입원교육과 퇴원교육으로 구분되었는데, 입원교육은 신생아집중치료실의 환경과 장비에 대한 기본적인 안내와 미숙아의 개념과 미숙아 특성의 이해 등이 포함되었고, 퇴원교육으로는 수유와 영양, 목욕시키기 등과 같은 기본 돌봄, 질병관리, 자극과 발달 교육, 그리고 부모를 위한 정서적지지 등이 포함되었다. 최근에는 미숙아가 처한 특수한 질병과 구체적인 상황에 맞는 교육이 더욱 필요한데, 호흡곤란(Lee, Oh, et al., 2010), 미숙아 망막증, 약시, 고도난시 등의 안과질환, 위식도역류, 서혜부 탈장, 경련 등과 같은 증상과 질병관리에 대한 교육이 이루어져야 한다(Yoon, 2007). 특히 Fanaroff와 Martin (2002)은 신생아집중치료실에서 퇴원한 아동들을 장기적으로 추적한 결과 발달장애, 학습장애, 과다행동 등의 빈도가 만삭아에 비해서 의미 있게 높아 자극과 발달 교육이 지속되어야 한다고 주장하였다. 미숙아 부모들 역시 단순한 양육 관련 문의보다도 미숙아의 장기적인 예후와 관련되는 발달문제, 장애여부 확인, 재활물리치료 등에 관심이 높다(Lee, 2009).
국외 연구를 살펴보면 Willis (2008)는 언어병리학자, 물리치료사, 전문 마사지사, 전문 운동관리사 등 각 분야의 전문가를 팀으로 구성하여 가정방문교육을 실시하고 효과가 있었다고 보고하였다. 이처럼 미숙아 돌봄 교육 프로그램에서 여러 분야의 전문가들이 팀 접근을 한다면 보다 전문적이고 효과적인 교육이 이루어질 것이다. 그리고 후유장애의 가능성이 있는 미숙아의 부모에게는 사회 ㆍ 경제적인 측면의 실질적인 정책 지원이 필요하며(Han, 2001; Lee, 2009; Lee & Kim, 2008; Park & Rhee, 2007), 미숙아 돌봄 교육 내용에는 언제든지 지원을 요청할 수 있는 의료기관과 정부기관의 접근 방법과 절차를 소개하는 내용이 포함되어야 할 것이다. 한편 이러한 다학제적이고 장기적인 돌봄에 대한 효과를 검증하기 위해서는 추적관찰이 필요하다. 추적관찰은 미숙아의 성장과 발달장애 및 미숙아에게 생길 수 있는 여러 가지 합병증을 조기에 발견하고 조치를 취하고 예후 및 장기계획에 대해 부모와 상담하며 의료인 자신도 피이드백을 시킨다는 점에서 의의가 있다(Choi, 2008).
본 연구에서 미숙아 돌봄 교육의 효과는 미숙아의 건강증진과 부모의 긍정적인 변화에 초점을 맞추고 있었다. 미숙아의 신생아집중치료실 입원시부터 부모의 반응을 파악하고 현 상황에 적응 할 수 있도록 돕는 것은 미숙아 어머니의 스트레스(Jang, 2005; Jung, 1999; Kim & Shin, 2010; Kwon & Kwon, 2007)와 불안(Lee, Oh, et al., 2010) 감소에 효과가 있었다. 또한 미숙아 돌봄 교육의 효과는 어머니의 역할자신감, 역할만족도, 역할수행 등의 증대로 확인하기도 하였는데, 미숙아 돌봄 교육이 궁극적으로 미숙아의 성장발달과 건강증진을 추구하는 것임을 감안할 때 여러 각도에서 미숙아의 건강을 평가할 수 있는 다양한 도구의 개발이 필요하다.
미숙아 돌봄을 위한 부모 교육의 환경적인 측면을 교육시기와 교육장소, 교육매체로 나누어 보았을 때, 먼저 미숙아의 부모 교육이 가장 많이 시행되어진 연구의 시기는 퇴원시기부터 1주일까지였다(Jang, 2005; Han, 2001). Lee (2009)는 미숙아 돌봄에 대한 집중적인 교육이 필요하다고 판단되는 시기는 출산부터 신생아집중치료실 입원, 그리고 퇴원 후 가정에서의 6개월까지라고 하였다. 본 연구결과 입원부터 퇴원 후 6개월까지(Lee, 2009), 또는 퇴원일부터 교정나이 3개월까지(Han, 2001) 비교적 오랜 기간 미숙아 돌봄 교육을 한 연구도 있었으나 대부분의 연구에서 단기적이었다. 미숙아 어머니의 역할자신감은 출산과 더불어 자동적으로 생기는 것이 아니라 분만 후 실제로 아기를 돌보는 활동을 통해 점차적으로 학습되며(Jang, 2005), 미숙아의 건강도 단기간에 평가할 수 있는 것이 아니기 때문에 단기간의 교육보다는 시범과 실제 수행을 통한 중재가 퇴원 후에도 지속적으로 이루어져야 할 것이다. 국외 연구에서도 미숙아 영아 초기의 신경학적 발달에 국한된 교육이 아닌 청소년기와 성인기에 걸친 장기적인 신경학적 발달 교육을 수행하고 있었다(Watson, 2010). 그리고 미숙아 장기적인 발달을 추적하며 장기적이고 지속적인 교육을 위해서는 병원뿐만 아니라 지역사회에서도 쉽게 접근할 수 있는 쾌적한 장소가 마련되어야 할 것이다.
교육매체 활용은 1920년대의 시각매체, 1950년대의 라디오, 1960년대의 TV, 1970-80년대의 컴퓨터, 그리고 1990년대 이후 멀티미디어와 웹에 관련된 연구까지 변화해 왔다(Hong, 2004). 1990년대 이후 많은 간호교육에서 소책자와 동영상을 주로 사용하였는데, 본 연구에서 Han (2001), Lee와 Kim (2008), Kwon과 Kwon (2007)은 주로 전화를 이용하여 미숙아 부모를 교육하고 상담하였고, Lee와 Oh 등(2010)은 반복교육과 인지적 강화를 위한 워크북을 통해 미숙아 어머니의 불안감소를 도모하였다. 최근에는 멀티미디어와 웹 기반을 통한 교육 자료 개발도 진행되고 있고(Lee, Oh, et al., 2010), 스마트폰 어플리케이션을 사용하여 미숙아 영양 관련 교육 프로그램이 개발되기도 하였다. 그 외에 e-Learning (Lee & Kim, 2008)이나, 인터넷 커뮤니티를 통하여 지속적인 교육과 사회적 연결망이 가능하게 한 연구(Kim & Shin, 2010; Lee, 2009)도 있었다. De Gagne와 Oh (2012)는 최근에는 가상세계를 활용하여 건강한 생활습관이나 특정 질병관리와 같은 교육이 이루어지고 있다고 소개하였다. 학습자로서 미숙아 부모도 그 세대가 변화함에 따라, 단순한 정보전달보다는 학습자가 지식을 능동적으로 구성할 수 있도록 유용한 테크놀로지를 활용하여 학습을 향상시킬 필요가 있다(De Gagne & Oh, 2012). 최근 스마트기기 등의 발달은 교수자의 효율적인 수업뿐만 아니라 학습자의 흥미를 유발하고 촉진할 수 있으며(Kim, 2012) 병원뿐만 아니라 원하는 곳에서 언제든지 쉽게 접할 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 그러므로 미숙아 돌봄을 위한 미숙아 부모 교육에서도 정보의 접근성, 부모의 기호, 교육매체의 다양화에 맞춰 교육을 실시한다면 교육의 효과를 극대화시킬 수 있을 것이다.
향후 미숙아를 돌봄 부모 교육 프로그램은 미숙아 어머니, 아버지, 그리고 미숙아를 돌보는 조모 등 다양한 교육 대상자에게 적합한 맞춤식 교육으로 개발되어야 하며 개발과 교육을 직접 담당하는 간호사의 전문적인 역할이 인정되어야할 것이다. 교육내용으로는 미숙아의 기본 돌봄, 특수 질병관리, 자극과 발달교육과 정서적지지 외에 언제든지 지원 요청할 수 있는 의료와 정부기관의 접근방법이 포함되어야 하며 다양한 측면에서 교육의 효과를 평가할 수 있는 도구의 개발이 필요하다. 이러한 미숙아 돌봄 교육은 입원직후부터 지속적으로 실시하되 추적관찰 할 수 있어야 하고 장기적인 발달증진을 위해 다학제적으로 접근해야한다. 최근 획기적으로 발전된 정보통신기술을 이용한 다양한 교육매체의 개발로 부모 교육의 효과를 극대화시켜야 하며 이를 위한 간호전문인력의 확보가 뒤따라야할 것이다. 본 연구 결과를 토대로 보다 효율적인 교육매체와 교육환경에서 미숙아 돌봄을 향상시킬 수 있는 프로그램의 개발을 제언하는 바이다.
결론
본 연구는 지금까지 국내에서는 시행된 바 없는 통합적 문헌고찰의 방법을 이용하여 미숙아 부모를 대상으로 미숙아 돌봄 교육을 시행한 국내 연구논문 16편을 분석하고 그 구성요소를 확인하고 논의한 것이다. 각 연구논문의 의미 있는 결과를 통합한 결과 부모의 미숙아 돌봄 교육은 인적요소, 학습요소, 환경요소로 구분되는 일반적인 교육의 구성요소와 마찬가지로 3가지 구성요소로 분류되었다. 즉, 교육자로서의 간호사와 학습자로서의 부모, 미숙아 돌봄 교육 내용과 교육효과, 그리고 교육 매체, 시기, 정소를 포함한 교육환경으로 나타났다. 본 연구를 통하여 교육자로서의 간호사의 역할에 대한 인정과 미숙아를 돌보는 주양육자인 부모를 포함하여 다양한 양육자가 있으며 이들의 교육수준과 경험은 각기 다르기 때문에 맞춤식 교육프로그램의 필요성이 대두되었다. 뿐만 아니라 입원부터 퇴원시, 그리고 미숙아의 추후발달에 대한 추적관찰이 매우 중요하기 때문에 미숙아 돌봄 교육은 일회성에 그치지 않아야하며 병원과 지역사회로 확대되어 지속적인 교육 프로그램의 개발이 되어야 함을 강조하였다. 본 연구는 부모의 미숙아 돌봄 교육에 대한 개요와 정확한 결론을 도출함으로써 향후 미숙아 돌봄 교육에 대한 좀 더 깊은 이해와 교육 프로그램 개발의 지침이 될 것이다.